
Corporate Taxes in the UK
Corporate tax in the UK is levied on the profits earned by limited companies, foreign companies with a UK branch, and unincorporated associations, including clubs and cooperatives. It is one of the largest sources of government revenue, and businesses are required to pay tax on their profits after deductions like allowable expenses, capital allowances, and other reliefs. This blog provides complete information on corporate tax’s various components, including who needs to pay it, how it’s calculated, and the key strategies businesses can implement to navigate the corporate tax landscape in the UK.
Importance of Understanding Corporate Tax for Businesses
Understanding corporate taxes in the UK is critical for businesses, whether large corporations or SMEs. Not only does this knowledge ensure compliance with tax laws, but it also helps identify opportunities for tax relief and minimize liabilities. Proper corporate tax planning can impact overall profitability and even provide a competitive edge through the efficient management of resources.
Who Needs to Pay Corporate Taxes?
Any UK-registered company, as well as foreign companies with a UK presence, must pay corporation tax. Non-profit organizations engaging in profit-generating activities may also owe corporate taxes on their profits. However, smaller businesses, like sole traders or partnerships, are not subject to corporation tax but may face income tax and other taxes.
Current Corporate Tax Rates in the UK
Overview of Current Tax Rates
As of 2024, the UK operates a tiered system for corporate tax rates. Companies with profits up to £50,000 pay a lower rate of 19%. For companies with profits exceeding £250,000, the rate is 25%. Businesses with profits between £50,000 and £250,000 fall under marginal relief, where the effective rate is between 19% and 25%.
Breakdown of Rates for Different Profit Levels
- 19% – For companies with profits up to £50,000.
- 25% – For companies with profits over £250,000.
- Marginal Relief – For companies with profits between £50,000 and £250,000, resulting in a sliding scale between 19% and 25%.
Changes in Rates Over the Past Years
In the past few years, the corporate tax rate has seen several adjustments. Before April 2023, all companies were taxed at a flat rate of 19%. However, to align with the broader fiscal goals and revenue needs of the government, the 2023 budget introduced the two-tier system. These changes underscore the importance of staying updated on evolving tax laws.
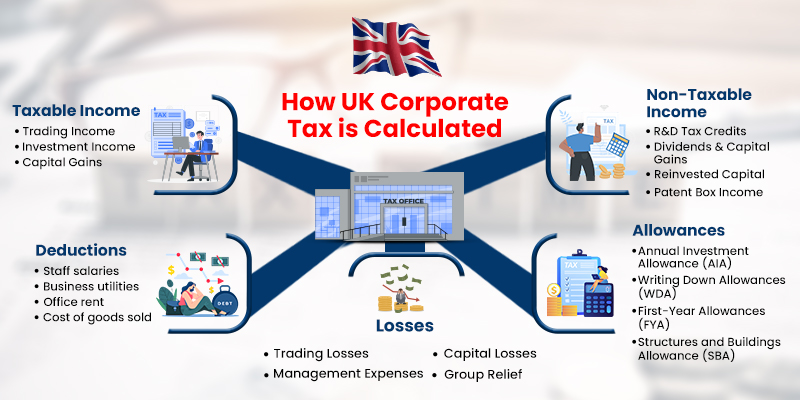
How Corporate Tax is Calculated
Taxable Profits vs. Non-Taxable Income
Corporation tax is charged on taxable profits, which includes trading income, investment income, and capital gains. Non-taxable income might include certain grants or capital that has been reinvested back into the company, depending on specific tax reliefs or allowances.
Deductions and Allowances
To calculate corporate tax, businesses can subtract allowable expenses, such as staff salaries, business utilities, office rent, and the cost of goods sold, from their total income. In addition to general expenses, specific allowances, such as capital allowances, allow businesses to claim tax relief on capital investments.
Losses and Their Impact on Tax Calculations
Companies that operate at a loss can carry these losses forward to offset future profits or carry them back to previous years to claim a refund on taxes paid. This provides valuable relief for companies that may experience fluctuating profits.
Filing Corporate Tax Returns
Deadlines and Key Dates
Corporation tax returns, known as a CT600, must be filed with HMRC within 12 months of the end of the accounting period. The payment of the tax itself is due within nine months and one day of the accounting period’s end. Missing these deadlines can result in penalties.
Filing Process and Requirements
Companies are required to file their returns online using HMRC’s digital platform. Businesses must also provide detailed information about their income, expenses, and any deductions or reliefs claimed during the period.
Penalties for Late Filings
Failing to file corporation tax returns on time results in penalties, which start at £100 for being one day late and escalate the longer the delay continues. For more significant delays or deliberate inaccuracies, fines can be substantially higher.
Deductions, Reliefs, and Allowances
R&D Tax Relief
Research and Development (R&D) tax relief is one of the most valuable reliefs available to UK companies. It is designed to encourage innovation and allows companies to deduct up to 230% of qualifying R&D costs from their taxable profits.
Capital Allowances
Capital allowances enable companies to claim tax relief on investments in assets such as machinery, equipment, or property. The Annual Investment Allowance (AIA) lets companies deduct the cost of most plant and machinery from their profits, up to a limit of £1 million.
Loss Relief
Businesses that have made losses can claim relief to offset their tax liability by carrying the loss forward to reduce future taxable profits or backward to reclaim tax paid in prior years.
Patent Box and Other Relief Schemes
The Patent Box allows companies to benefit from a reduced 10% tax rate on profits generated from patented inventions, encouraging businesses to invest in innovation.
Tax Implications for SMEs vs. Large Corporations
Differences in Tax Obligations
While all businesses are subject to corporation tax, SMEs and large corporations may face different obligations. SMEs can take advantage of more reliefs and allowances, including specific schemes like R&D relief, while larger corporations often have more complex tax situations involving international aspects and transfer pricing rules.
Special Schemes or Allowances for SMEs
Small and medium-sized enterprises benefit from special allowances like Enhanced Capital Allowances and Simplified Reporting, reducing their administrative burden.
Tax Planning Strategies for Both
Both SMEs and large corporations can implement tax planning strategies to minimize their tax liabilities. This may involve deferring income, maximizing deductions, and ensuring compliance with changing tax laws.
International Aspects of Corporate Taxation
Taxation of Foreign Profits
UK-based companies are generally taxed on their worldwide profits. However, double taxation relief is available to avoid paying tax twice on the same income.
Double Taxation Treaties
The UK has an extensive network of double taxation treaties that helps businesses operating in multiple countries to avoid being taxed in both jurisdictions. This is crucial for international corporations that generate income across different regions.
Transfer Pricing Rules and Compliance
Transfer pricing rules ensure that companies set fair prices on transactions between related entities. Businesses operating across borders must adhere to these rules to prevent tax avoidance through inflated or deflated pricing of goods and services.N
Upcoming Changes and Trends in UK Corporate Tax
Expected Reforms or Changes in Tax Law
The landscape of UK corporate taxes is always evolving. Recent discussions focus on reducing loopholes in the tax system and ensuring multinational corporations contribute their fair share. It’s essential for businesses to stay updated on any new reforms to avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
Impact of Brexit on Corporate Taxation
Brexit has brought about significant changes in the way UK businesses operate, particularly those with EU ties. New trade agreements and regulatory changes may affect how corporate taxes are calculated for international businesses.
Corporate Tax Planning and Strategies
Importance of Tax Planning for Businesses
Tax planning is a critical aspect of financial management for businesses of all sizes. Effective planning can reduce the amount of tax payable, ensure compliance with tax regulations, and enhance the overall financial health of the company.
Tips for Reducing Corporate Tax Liability
- Maximize deductions – Ensure that all allowable expenses are claimed.
- Use reliefs – Take advantage of R&D tax relief, capital allowances, and loss relief.
- Defer income – If possible, defer income to the following tax year to spread tax liability.
Working with a Tax Advisor or Accountant
To effectively navigate the complexities of corporate tax in the UK, businesses are advised to work with tax advisors or accountants who can provide expert advice, handle compliance, and help in tax-efficient structuring.
Conclusion
Understanding corporate taxes in the UK is essential for maintaining compliance and optimizing business operations. By familiarizing themselves with tax rates, deductions, reliefs, and filing requirements, businesses can minimize their liabilities and maximize profits.
Given the complexities of corporate taxation, especially with the evolving regulatory landscape, seeking professional advice is a wise decision. It ensures businesses remain compliant while also identifying opportunities to save on taxes.
For expert corporate tax advice and services in the UK, contact us today. Learn more about tax-efficient strategies tailored to your business and ensure your company is compliant with all UK tax regulations. Our team of specialists is ready to help you maximize savings and minimize tax liabilities.
