
Recent amendments relating to Schedule III relating to enhanced disclosure requirements in financial statements (under the Companies Act 2013)
Recent amendment
1. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs issued separate notifications on 24th of March 2021 with a view to promote transparency and accountability in company financial statement, whereby, it brought about changes in the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules 2014 (Audit Rules) and also in the Companies (Accounts) Rules 2014 (Accounts Rules) and in Schedule III of the Companies Act 2013.
Applicable date of amendments
2. These amendments are applicable with effect from first April 2021. This means, the financial statements prepared by the company for the financial year 2021-22 will be based on the above notification. However, one should take note that the company needs to show comparatives figure for the financial year 2020-21(previous year figures) in the financial statements of 2021-22. Therefore impact of the additional disclosure need to be assessed with effect from financial year 2020-2021 itself. .
Changes arising out of the amendment
2.1 There are two aspects arising out of this amendment
| 1. | First One | There would be changes in Schedule III – i.e., in the format of financial statements of companies complying with Indian Accounting Standards (IndAs) coupled with its schedules with more disclosures and |
| 2. | Second One | There would be also changes in the Audit Report arising out of Audit Report Rules such as (i) regrouping the current disclosures (iii) additional new disclosures and (iii) integrated approach in disclosure between Schedule III and CARO 2020. |
Applicability of Schedule III of the Companies Act 2013
3. Schedule III is applicable for the following three segments whose financial statements are
| 1 | Companies governed by AS Rules 2006 | Applicable to Companies whose financial statements are drawn up with the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006. |
| 2 | Companies governed by IndAS Rules 2015 | Applicable to Companies whose financial statements are drawn up in compliance with the Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015. |
| 3 | NBFC companies | Applicable to Companies who fall in the scope of Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) whose financial statements are drawn up in compliance with the Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015. |
prepared and audited and presented to the shareholders.
Applicability of Indian Accounting Standards
4. The Government of India and the Ministry of Corporate Affairs brought out a notification related to the adoption and applicability of Indian Accounting Standards by all companies in India. This notification was brought through a legislative enactment Companies (Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS)) Rules 2015.
As per the above notification, all companies are required to adopt the IndAs in a phased manner starting from the financial year 2016-17. Ever since the above enactment, there have been couple of amendments in the notifications including the recent one.
Amendments relating to companies following the IndAS
5. Since almost all the companies are now preparing the financials as per the Indian Accounting Standards (IndAS), let us discuss the amendments pertaining to IndAS. There are no amendments relating to profit and loss accounts and amendments are only in respect of balance sheet.
The main purpose of this amendment
6. Notification issued by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, is intended more towards:—
- to know the real ultimate beneficiary in cases where the investments are made through conduits and much more transparent and
- adequate disclosures in areas like promoter shareholdings,
- MSME payments,
- increased disclosure on trade receivables and trade payments,
- loan and advances given to promoters, directors, KMPs and related parties,
- increased disclosures on capital work-in-progress of projects including the projects which have been delayed and suspended,
- details on benami properties held,
- details of borrowings based on the security of current assets from banks and financial institutions,
- details relating to wilful defaulters,
- relationship of companies with struck off companies and increased disclosures,
- status of delayed charge filing / medication and satisfaction with reasoning,
- number of layers of company,
- disclosures of important ant financials ratios and many more disclosures
Amendments at a glance
7. There are three major amendments which has been brought in the amendments as discussed below:—
| A | Regrouping of certain balance sheet items | |
| (a) | Under current liabilities borrowing | The long-term borrowings of current maturities are to be now regrouped under borrowing. |
| (b) | Under current liabilities Loans | Security Deposit which is currently shown as loan is to be regrouped as other Financial Assets |
| (c) | Under current liabilities Lease | Other financial liabilities which includes lease liabilities are now required to be regrouped under Lease Liabilities |
| B | Integrated approach in disclosure between Schedule III and CARO 2020 | |
| By the recent amendment, schedule III is now adopting an integrated approach between the disclosures of Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, 2020 (CARO 2020) and Schedule III. This integrated approach would greatly facilitate for statutory auditors since they are required to report in CARO 2020 on similar matter in their Audit Report. | ||
| C | New disclosures now required | |
| Many new disclosures that have been mandated in the revised Schedule III, in order to bring more transparency and also enhance the quality of the financials, which would greatly facilitate the recipients of the financial statements. |
A. Regrouping of certain balance sheet items
8. The following are the regrouping arising out of the amenments to be which are required to be disclosed in the financial statements of the company.
| Items in balance sheet | Before the amendment | After the amendment |
| Heading current liabilities –Current maturities of long term borrowing | Current maturities of long term borrowing are disclosed by clubbing with the heading “other financial borrowing” and long term borrowings are shown under the heading “borrowing” separately. | After the amendment, Current maturities of long term borrowing is required to be regrouped under the heading “borrowings” |
| Heading current assets – Security deposit | Security deposits are disclosed as part of “loans” | After the amendment security deposits are to be separately regrouped as “other financial assets” |
| Heading current liabilities – Leases liabilities | Lease liabilities of non-current and current parts form part of “other financial liabilities” | After the amendment the lease liabilities under non-current and current will have to disclosed separately on the face of the balance sheet as under:— Non-current liabilities – Lease liabilities Current liabilities – Lease liabilities- current |
B. Integrated approach in disclosure between Schedule III and CARO 2020
9. The companies are now required to provide the required information in the financial statements which in turn would be aligned along with information disclosed in the Companies Auditor’s Report Order 2020 (CARO 2020)
| Sr. No. | CARO2020 | CARO2020 | Disclosures in the financial statements in alignment with CARO2020 |
| Clause No. | Reporting Subject | ||
| 1 | 3(i)(c) | Property, plant and equipment not held in company’s name | Disclosure in the specified format to be made by companies relating to the details of immovable property where title deeds are not held in the name of the company. (this disclosure is for, other than properties where the company is the lessee and the lease agreements are duly executed in favour of the lessee) |
| Property, plant and equipment – cases where fair valuation of investment is carried out | Disclosure is required whether the fair value of investment property is based on the valuation done by the registered valuer as per the provisions of Rule 2 of Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation) Rules, 2017. | ||
| Property, plant and equipment and intangible assets – cases where revaluation is done | Disclosure is called for as to whether the revaluation is based on the valuation done by the registered valuer as per the provisions of Rule 2 of Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation) Rules, 2017. | ||
| 2 | 3(iii) and 3(iv) | Loans given by company & to director | Disclosure is required to be made by the company in the specified format in cases where loans and advances in nature of loans are repayable on demand / are given without specifying any term / period of repayment to directors, key managerial personnel and also to related parties. |
| 3(iv) | Investments, loans and advances given (number of layers) | Under the provisions of clause (87) of section 2 of the Companies Act 2013 read with Companies (Restriction on number of Layers) Rules, 2017, if the company has not complies with the number of layers of investment prescribed, then the disclosure is required to be made with the name of the company along with CIN of the companies beyond the specified layers and the relationship or extent of holding of the company in such downstream companies. | |
| 3 | 3(viii) | Unrecorded transactions arising out of Tax assessments |
Any income of the company which has not been recorded but which arises during the course of Income Tax assessment or other tax assessments, shall be disclosed unless any scheme exempts this disclosure. Also, any previously unrecorded income or assets have been properly recorded in the books of account. |
| 4 | 3(ix)(b) |
Repayment of Loan – wilful default | Disclosure is required to be made by the company in case the company has been declared as a “wilful defaulter” by any bank, financial institution or other lender, providing the details of date of date of declaration along with details of defaults by the company. |
| 5 | 3(ix)(c) |
Repayment of Loan – utilisation of borrowed funds: | Following disclosures are called for where the funds are given/received by a company which are to be given as loan, investment, security or guarantee to a third company via an intermediary company to the ultimate beneficiary. Disclosure is required to be made by the company and as well by the intermediary company. Disclosure called for is – the details of funds exchange, – details of ultimate beneficiaries and compliance with Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999& – Prevention of Money Laundering Act 1992. |
| 6 | 3(i)(e) |
Property, Plant & Equipment – proceeding against company under benami transactions | Under the Benami Transactions (Prohibition) Act, 1988, any proceedings has been initiated / pending against the company, then the company needs to disclose the details as under:- -property, amount, -beneficiary details, -whether it is recorded in the books of accounts or not and -nature of proceedings and company’s view on the same |
| 7 | 3(ix)© |
Borrowing from banks and financial institutions – usage of funds for particular purpose or otherwise. | If funds borrowed from banks and financial institutions are not used for the specified purpose for which they are raised, disclosure of where the funds have been used is required to be made. |
| 8 | 3(xx) | Corporate Social Responsibility | Relating to CSR expenditure by the company, in case of shortfall, details of shortfall for current year and cumulative shortfall amount are to be disclosed along with the reasoning for shortfall. |
C. New disclosures now required
10. The new disclosures now called for as per the recent amendments are as under:-
10.1. Share Capital
This amendment has now harmonized the Regulation 31 of Securities and Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015 which specified that the listed entities are required to make the disclosures relating to promoter’s holding. The disclosures now to be made by the companies are relating to details of promoter holdings as per the following format:-
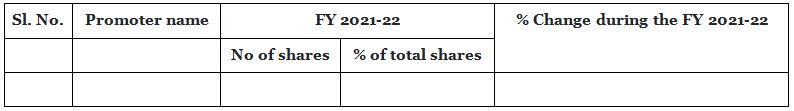
10.2. Trade Payables
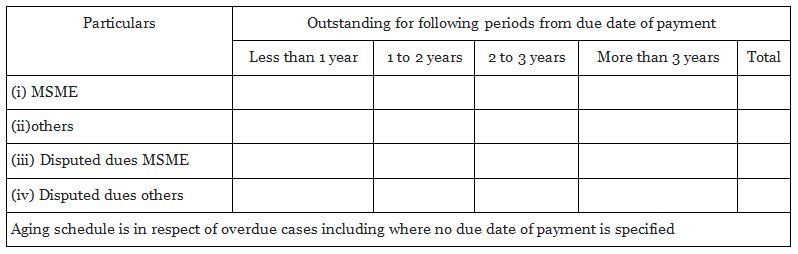
As per the amendment, the disclosure is called for in relating to trade payables which disclosed by doing ageing analysis which is introduced for the first time in this amendment in the notes attached to the financial statements. Also, the disclosures are required to be made on specified base of certain class of creditors. The format for this disclosure is as given below:-
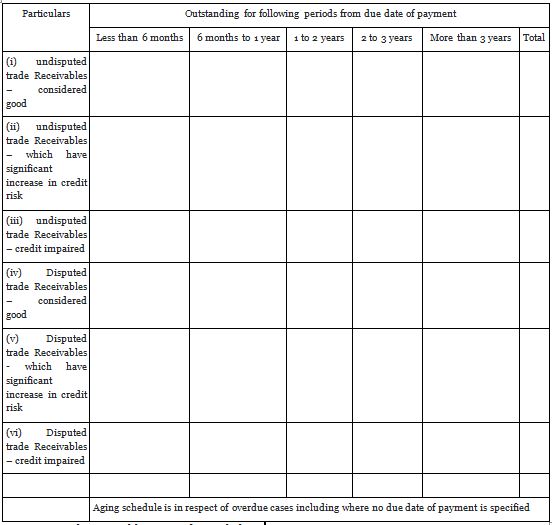
10.3. Trade Receivables: On the same line discussed above, the disclosure is also required to be made in respect of trade receivables as per format below:-
10.4. Statement of current assets filed with banks and financial institutions for borrowing facilities:
This disclosure is also brought in for the first time in notes to financial statements. As per this amendment, the company has to make disclosure as to whether the statements of current assets filed with bank and financial institutions for borrowings are in agreement with books of account.
The reconciliation and description of material discrepancies are required to be given in cases of non-agreement of the statements provided to the bank / financial institutions with the books of accounts maintained by the company.
10.5.Capital work in progress (CWIP) and Intangible assets under development (IAUD).
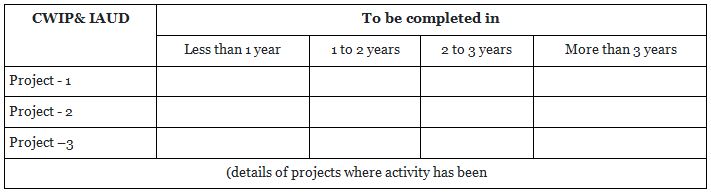
10.5.1 The details on the above are required to be disclosed in the notes to financials with ageing disclosure for capital work in progress and intangible assets under development as per format given below:-
This disclosure is also one of the first time introduction to the financial statements. Separate disclosure is called for projects which are suspended by the company. The company may have to share the details with the auditors about the parameter of each project, cost details, cost overrun and time overrun etc., as against the budgeted cost and time plan. Without providing the above details to auditors, it would be difficult to make the disclosures. The company and the auditors have to work together after sharing the required details so that the required compliance could be met.

10.5.2 For capital work in progress (CWIP) and intangible assets under development (IAUD), whose completion is overdue or has exceeded its cost compared to its original plan, following details shall be given:
10.6. Accounting for Scheme of Arrangements
This disclosure is already being made by the auditors in their auditors report addressed to the members of the company and the current amendment calls for the disclosure of the same in the notes to the financial statements as well. There is also a requirement under the provisions of the Companies Act that the company is required to file a certificate obtained from the auditors stating that the terms of the scheme are in accordance with the applicable Accounting Standards while filing the Scheme of Arrangement with National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT),
Now, as per the current amendment, in addition to the disclosure given in the auditor’s report, the company is required to make a disclosure in the notes to financial statement, on the effect of such scheme of arrangements have been accounted for in the books of account of the company in accordance with the scheme and in accordance with accounting standards and any deviation in this regard is also required to explained in details.
10.7. Disclosure of Ratios
This disclosure is in line with the Schedule V ofSecurities and Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015 (SEBI LODR) which specified for listed companies that the details of significant changes (i.e., 25% or more) in key financial ratios to be given in the Management, Discussion & Analysis section in the Annual Report. Also, details of change in return on net worth to be disclosed irrespective of percentage change compared to previous year.
Disclosure called for in respect of following ratios:-
(a) Current Ratio,
(b) Debt-Equity Ratio,
(c) Debt Service Coverage Ratio,
(d) Return on Equity Ratio,
(e) Inventory turnover ratio,
(f) Trade Receivables turnover ratio,
(g) Trade payables turnover ratio,
(h) Net capital turnover ratio,
(i) Net profit ratio,
(j) Return on Capital employed,
(k) Return on investment
There is a requirement to disclose the elements forming part of numerator and denominator. Additionally, in case if there is more than 25% change in any ratio as compared to the preceding year, additional explanation is required to be given.
10.8. Relationship with Struck-off companies
Where the company has any transactions with companies struck off under section 248 of the Companies Act, 2013 the Company is required to make the following disclosure:-
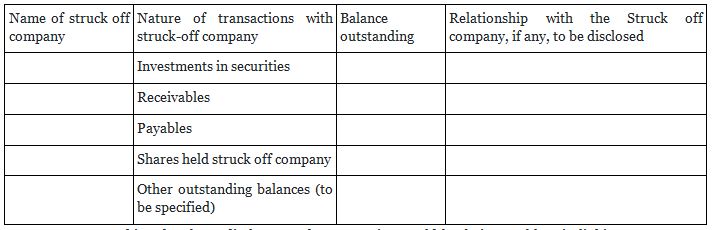
For making the above disclosures, the companies would be facing problem in linking to details of struck off companies unless the companies have a very strong IT support. This is going to be a big challenge for the company and as well for the auditors considering the large number of debtors and creditors.
10.9. Registration of charges or satisfaction with Registrar of Companies
Disclosure is called for in respect of any charges or satisfaction yet to be registered with Registrar of Companies beyond the prescribed time limit of statutory period – giving the details and the reasoning’s thereof for such delayed registration
10.10 Inclusion of prior period errors
Format of statement of changes in equity changed is required to include prior period errors column in equity share capital reconciliation.
10.11. Details of Crypto Currency or Virtual Currency
This disclosure is brought out in order to enhance the transparency in the financial statements in the absence of the clear guidelines on crypto currency. If company traded / invested in Crypto currency or virtual currency during the financial year, the following disclosure called for.
- profit or loss on transactions involving Crypto currency or Virtual Currency
- amount of currency held as at the reporting date,
- Deposits or advances from any person for the purpose of trading or investing in Crypto Currency/ virtual currency.
11. Conclusion
Probably, considering the past corporate failures, the regulators have taken the step of more and more transparent disclosures and strengthening the system of financial reporting. Many reporting details would call for the usage of IT tool and techniques for the purpose of auditing and as well reporting from the side of auditors and as well as from the side of audited.
It may also be noted that the provisions which are now brought out is not only casting responsibility on the part of the directors of the company, but equally on the auditors as well. The auditors are required to substantiate the disclosure statements made by the directors in the financial statements, by applying their audit procedures and issue their independent auditors report to the shareholders of the company.
One can say that Ministry of Corporate Affairs is bringing out increasing stringency in compliance by way of adding numerous additional disclosures in the financial statements of the company and audit report in order to have much more transparency. No doubt, the board report also would have reflect the changes and bring out more disclosures.
There is no doubt that we are moving towards much more additional disclosures which would definitely improve the qualities of financial statement of the companies but at the same time it will increase the cost of compliance as well with more and more increased disclosures – especially to smaller companies.
You might also be interested in : Financial Consultancy Firm in India | Top Audit Firms in India | GST Consulting Services
